Characteristics of armature
Fiberglass and steel rebar features: comparison
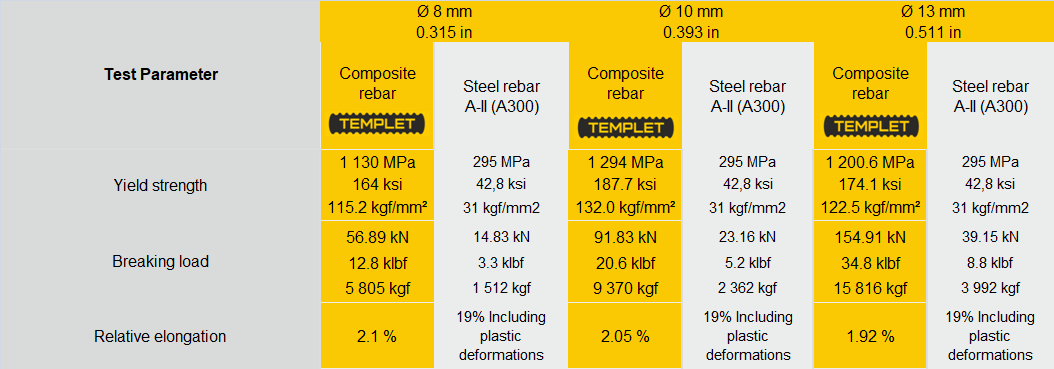
Comparirison of fiberglass and metal rebar

Possible replacement of steel rebar by FRP rebar according to standard tensile strength

How to use this table: For example - The customer uses A500 brand reinforcement with a diameter of 16mm. To select the interchangeable FRP rebar, you need to find your brand in the “Type of rebar” line, in our example it is A500. Next, in the column below we look for our diameter - 16. Then in the line on the right we find the diameter of the interchangeable composite reinforcement - 10.
The proposed replacement of steel rebar with FRP rebar is advisory in nature. For structural construction, it is recommended to confirm the replacement with engineering calculations that take into account the nature of the structure loading . This is not a public offer.
Relationship between stress and strain

Force versus displacement for ø10mm rebar

Other features of composite (FRP) rebars
Density.
2140 kg/m3.
Coefficient of thermal linear expansion.
- steel rebar 13-15 x10-6/°С
- fiberglass rebar 9-12 x10-6/°С
- concrete 7.4-10 x10-6/°C (depending on the concrete composition and properties of the constituent materials).
In other words, the composite rebar has a coefficient of thermal linear expansion that is almost similar to the coefficient of thermal linear expansion of concrete. This increases the service life of buildings.
Coefficient of thermal conductivity.
0.48 Вт/(м °С)
Heat resistance .
The rebar is hidden inside the concrete and has good heat resistance . While in concrete, FRP rebar maintains a load-bearing capacity of up to 300 ° C.
Durability.
Express tests show that the durability of such material is a hundred years or more. If necessary, we will be able to provide the results of such tests for such products.
Corrosion and physical properties.
Excellent corrosion resistance. Electromagnetic neutrality. Dielectric.
Chemical Resistance.
Acid resistance is excellent and there is no chemical reaction with acids. The alkali resistance test for composite rebar shows that the absence of solvents and other volatile components in the epoxy resin guarantees its excellent chemical resistance. Our rebars do not use any solvents or volatile components.
Chemical & Material Composition
The binder is based on high-quality epoxy resin, glass roving from world leading manufacturers in the industry. The size is optimally selected for ideal adhesion of fibers and binder.
Ultra violet resistance.
The special pigment in our rebar compositions evolves high resistance to ultraviolet radiation.
Frequently Asked Questions
The maximum number of floors in buildings using composite rebars is determined by the rules, standards and laws of the country where such a structure is being built, as well as relevant engineering calculations. The practice of using composite rebars, for example in the USA, extends to low-rise private buildings and, as a rule, these are buildings with a height of one or two floors.
Composite and steel reinforcement are similar in cost with the same diameter. But it should be taken into account that composite rebar is 2-4 times stronger than steel rebar, and four times lighter than it. Guided by the table for equal-strength replacement of FRP and steel rebars and engineering calculations, you can use FRP rebar of a smaller diameter. In this case, and also taking into account the reduction in transportation costs, it is possible to obtain a price gain of up to 30%.
© 2025 Templet. All Rights Reserved
